0-Bollinger-Symbol
Wed 12 November 2025
# Created: 20250104
import pyutil as pyu
pyu.get_local_pyinfo()
'conda env: py311; pyv: 3.11.9 (main, Apr 19 2024, 16:48:06) [GCC 11.2.0]'
print(pyu.ps2("requests"))
requests==2.32.3
import yfinance as yf
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Step 1: Download data
start = "1976-01-01"
end = "2013-12-31"
symbol = "^GSPC" # S&P 500
# Download historical data
data = yf.download(symbol, start=start, end=end)
# Step 2: Define a function to calculate Bollinger Bands
def bollinger_bands(price, window=20, num_sd=2):
rolling_mean = price['Close'].rolling(window=window).mean()
rolling_std = price['Close'].rolling(window=window).std()
price['Upper Band'] = rolling_mean + (rolling_std * num_sd)
price['Lower Band'] = rolling_mean - (rolling_std * num_sd)
price['Moving Average'] = rolling_mean
return price
# Apply the function
data = bollinger_bands(data)
# Step 3: Plot the data with Bollinger Bands
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(data['Close'], label='Close Price', color='blue')
plt.plot(data['Upper Band'], label='Upper Band', color='red', linestyle='--')
plt.plot(data['Lower Band'], label='Lower Band', color='green', linestyle='--')
plt.plot(data['Moving Average'], label='Moving Average', color='orange')
plt.fill_between(data.index, data['Lower Band'], data['Upper Band'], color='gray', alpha=0.2)
plt.title(f'Bollinger Bands for {symbol}')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
[*********************100%***********************] 1 of 1 completed
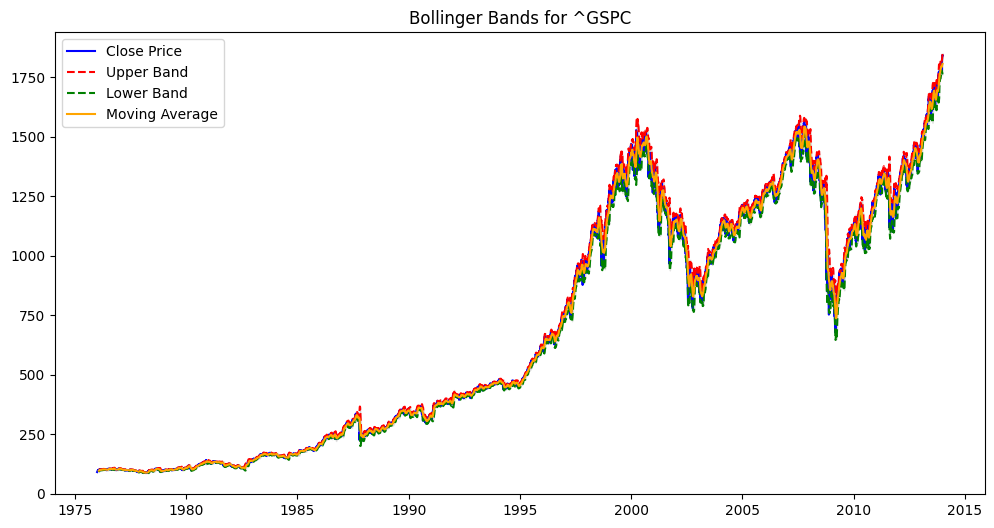
def show_bollinger_bands(symbol):
# Step 1: Download data
start = "1976-01-01"
end = "2013-12-31"
# Download historical data
data = yf.download(symbol, start=start, end=end)
# Step 2: Define a function to calculate Bollinger Bands
def bollinger_bands(price, window=20, num_sd=2):
rolling_mean = price['Close'].rolling(window=window).mean()
rolling_std = price['Close'].rolling(window=window).std()
price['Upper Band'] = rolling_mean + (rolling_std * num_sd)
price['Lower Band'] = rolling_mean - (rolling_std * num_sd)
price['Moving Average'] = rolling_mean
return price
# Apply the function
data = bollinger_bands(data)
# Step 3: Plot the data with Bollinger Bands
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(data['Close'], label='Close Price', color='blue')
plt.plot(data['Upper Band'], label='Upper Band', color='red', linestyle='--')
plt.plot(data['Lower Band'], label='Lower Band', color='green', linestyle='--')
plt.plot(data['Moving Average'], label='Moving Average', color='orange')
plt.fill_between(data.index, data['Lower Band'], data['Upper Band'], color='gray', alpha=0.2)
plt.title(f'Bollinger Bands for {symbol}')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
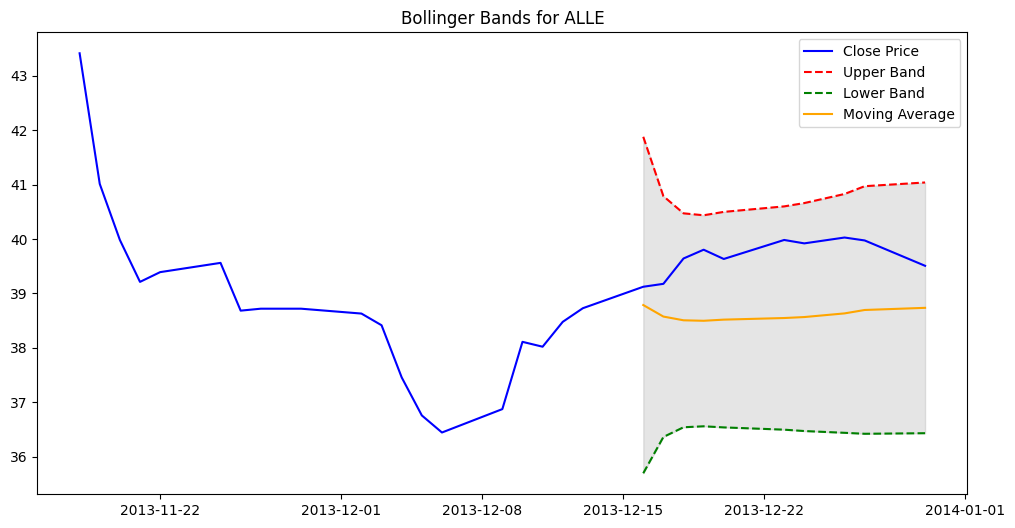
show_bollinger_bands("ALLE")
[*********************100%***********************] 1 of 1 completed
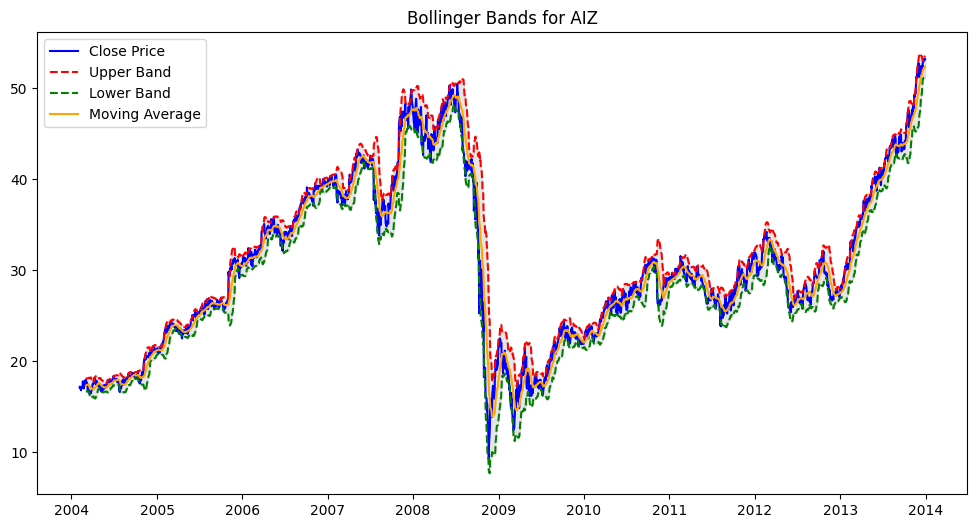
show_bollinger_bands("AIZ")
[*********************100%***********************] 1 of 1 completed
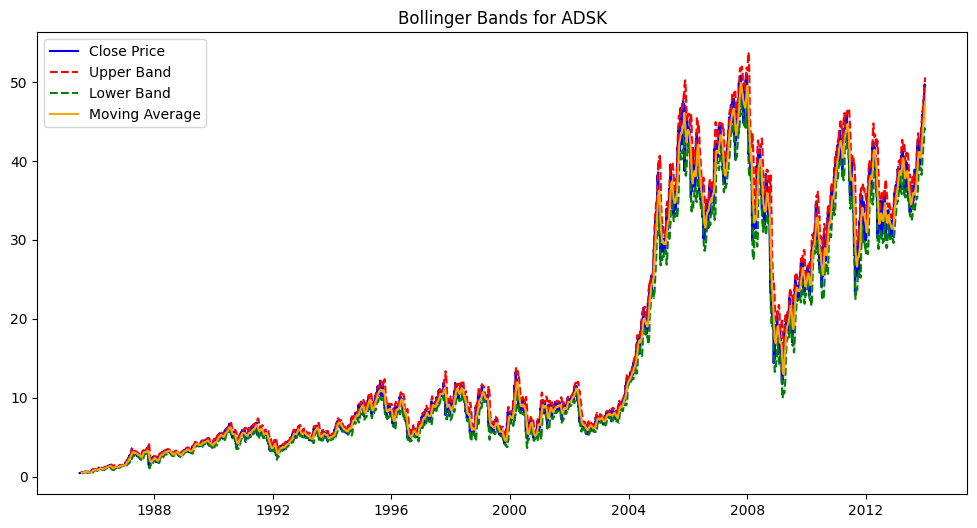
show_bollinger_bands("ADSK")
[*********************100%***********************] 1 of 1 completed
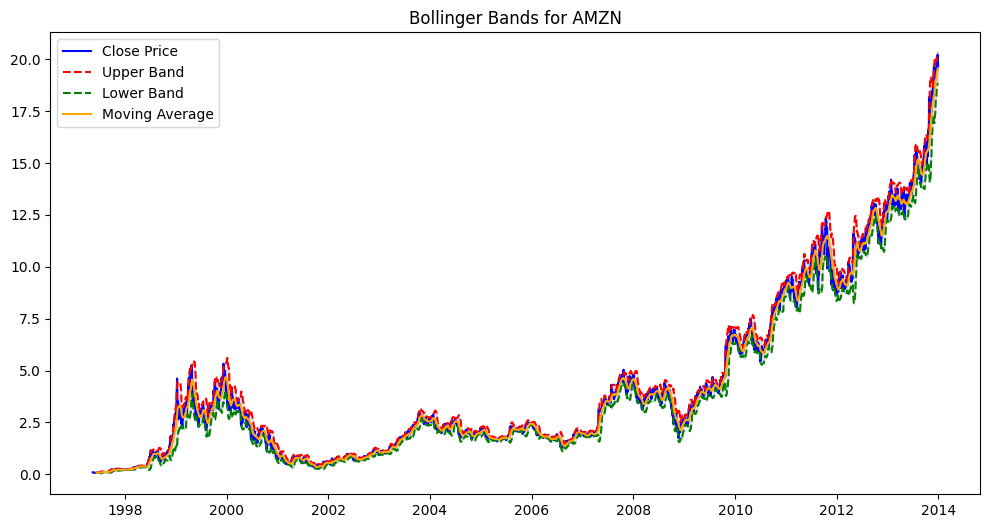
show_bollinger_bands("AMZN")
[*********************100%***********************] 1 of 1 completed
Score: 10
Category: stockmarket